Key to Fighting Head and Neck Cancer—Nutrition Therapy
Key to Fighting Head and Neck Cancer—Nutrition Therapy
Current medical research shows that up to 80% of head and neck cancer patients experience reduced food intake and weight loss due to complications such as mucositis caused by radiotherapy. Patients with moderate to severe malnutrition have significantly lower overall cure rates and a markedly higher risk of complications. Malnutrition not only reduces patients' quality of life but also weakens treatment efficacy, increases complications, and shortens survival.
The clinical guidelines of the Chinese Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (CSPEN), the European Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ESPEN), and expert consensus all emphasize that nutrition therapy must be initiated early and synchronously with comprehensive anti-cancer treatment. As the saying goes: “An army marches on its stomach!”

Below is a brief introduction to the principles of nutrition therapy for cancer:
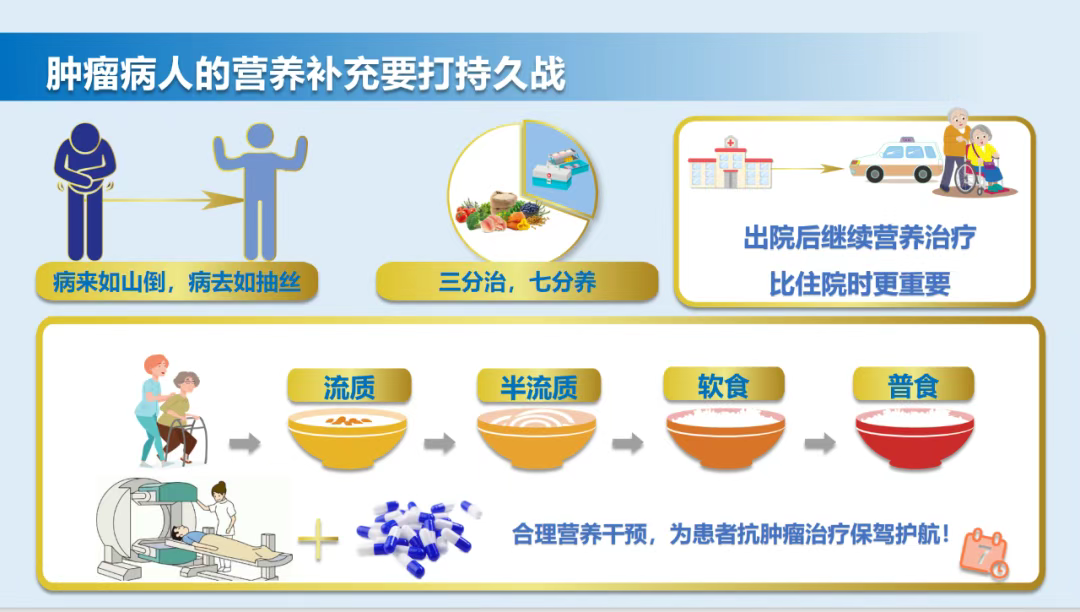
1.Personalized Plan: Develop a plan based on the patient’s baseline condition, tumor type, treatment stage, and nutritional status (e.g., weight change, blood indicators). It is recommended to consult a nutritionist before treatment for nutritional intervention.
2.Adequate Energy and Protein: Energy requirements are usually higher than those of ordinary people (approximately 25–30 kcal/kg/day) to avoid excessive weight loss. Protein intake should be sufficient (1.2–2.0 g/kg/day) to help repair tissues and maintain immunity. High-quality protein sources such as fish, eggs, dairy, lean meat, and soy products are recommended.
3.Balanced Diet: Ensure intake of carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Prioritize natural foods such as whole grains, fresh fruits, and vegetables.
4.Addressing Special Situations:Poor Appetite: Eat small, frequent meals; choose high-energy-density foods (e.g., nutritional powders, protein powders); adjust food flavors (e.g., sour or sweet tastes to stimulate appetite).Digestive Issues: For diarrhea, avoid greasy and raw/cold foods; for swallowing difficulties, purée foods or opt for liquid/semi-liquid diets.
5.Methods of Nutrition Therapy:Oral Nutritional Supplements: Use medical nutritional preparations (e.g., enteral nutrition powders/liquids) when natural food intake is insufficient.Enteral/Parenteral Nutrition: If oral intake or absorption is severely compromised (e.g., due to severe radioactive mucositis), nutrition can be provided via nasogastric tube (enteral) or intravenous infusion (parenteral) under medical guidance.
Precautions:
- Avoid Blind “Dietary Restrictions”: There is no need to excessively restrict so-called “trigger foods” (e.g., chicken, seafood) unless the patient is allergic to a specific food.
- Adjust Based on Treatment Stage: For example, during radiotherapy or chemotherapy, a temporarily lighter diet may be needed to reduce gastrointestinal irritation; gradually increase nutritional density during recovery.
- Monitoring and Adjustment: Regularly assess weight and dietary intake; adjust the plan based on the body’s response; consult a nutritionist if necessary.
Introduction to Department Experts

Chief Physician
Zhang Yingdong
Chief Physician, Clinical Director of the Third Department of Radiotherapy, Gansu Wuwei Cancer Hospital & Lanzhou Heavy Ion Hospital
Former Administrative Head of the Radiotherapy Department at Peking University International Hospital, Director of the Radiotherapy Center at Capital Medical University Sanbo Brain Hospital,Graduate of the Radiotherapy Oncology Program at Peking University Third Hospital.
With over 30 years of experience in tumor radiotherapy. Specializes in radiotherapy for malignancies of the central nervous system, head and neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis, and limbs. Has in-depth research on combining radiotherapy with chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and other comprehensive treatments. Expertise in developing personalized comprehensive treatment plans based on patients’ specific conditions. Possesses extensive clinical experience and profound academic accomplishments. Has published multiple papers in authoritative journals such as Cancer Cell International, Chinese Journal of Radiation Oncology, and Chinese Journal of Oncology, including “EGFR inhibitor C225 increases the radiosensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer cells,” “Research Progress on Vascular Injury Induced by Continuous Low-Dose Rate Irradiation,” “Study on the Radiosensitizing Effect of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody on Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines,” and “Research Progress on the Mechanism of Irradiation-Induced Tumor Cell Apoptosis.”
- Member of the Radiotherapy Professional Committee of the Bethune Charitable Foundation
- Member of the Central Nervous System Tumor Radiotherapy Group of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association’s Radiation Oncology Division
- Member of the Beijing Anti-Cancer Association’s Tumor Radiotherapy Professional Committee
- Member of the Head and Neck Tumor MDT Professional Committee of the Beijing Cancer Prevention and Control Society
Preliminary Review: Ma Shuqian
Final Review: Zhang Lihong
