Radiation Therapy: "Friendly Fire"? 90% Get It Wrong
Radiation Therapy = "Destroying 1,000 Enemies at the Cost of 800 Friendly Casualties"? 90% of People Misunderstand These Truths!
When it comes to "radiation therapy," many people's first reaction is fear: "Are the side effects particularly severe?" "Will it kill healthy cells?" "Wouldn’t it be better to avoid treatment altogether to spare the suffering?" In reality, these misconceptions about radiation therapy are causing many cancer patients to miss their optimal treatment window. Today, let’s dive deep into radiation therapy—clarifying the core knowledge to help you shed your fears.
Myth Clarified: Do the side effects of radiation therapy truly outweigh its benefits?
This is absolutely the biggest misconception about radiation therapy! With the rapid advancement of computer and imaging technologies, radiation therapy is no longer a "crude, broad-spectrum attack" but has evolved into a highly precise "targeted strike."
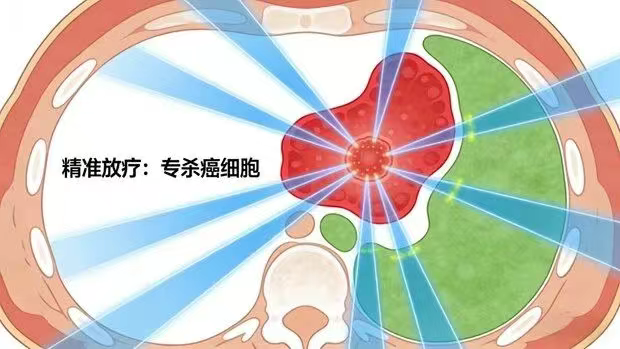
Modern techniques such as stereotactic radiotherapy, proton therapy, and heavy ion therapy can now concentrate high doses of radiation onto tumor tissues like precision-guided missiles, while surrounding normal tissues receive only minimal exposure. In simple terms, it’s about “targeting cancer cells while sparing healthy ones,” significantly reducing damage to normal tissues.
Moreover, radiation oncologists carefully evaluate the tolerance of normal tissues beforehand and provide timely symptomatic support, making the incidence of severe side effects quite low—so there’s no need to worry excessively.
Key Insight: What Exactly Is Radiotherapy?
Radiotherapy, surgery, and chemotherapy are known as the "three major pillars" of cancer treatment. According to statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO), 45% of malignant tumors can be cured, with radiotherapy contributing to 18% of these cures—second only to surgery (22%) and far surpassing chemotherapy (5%).

Unlike "systemic drug therapy," radiotherapy is a relatively non-invasive physical treatment. Its greatest advantage lies in its ability to destroy cancer cells while preserving the integrity and function of human tissues and organs as much as possible—this is crucial for improving the patient's long-term quality of life!
Scope of Application: When is Radiotherapy Needed? How Effective Is It?
Many people assume that radiotherapy is only a "last resort" option, but its uses are far broader than that.
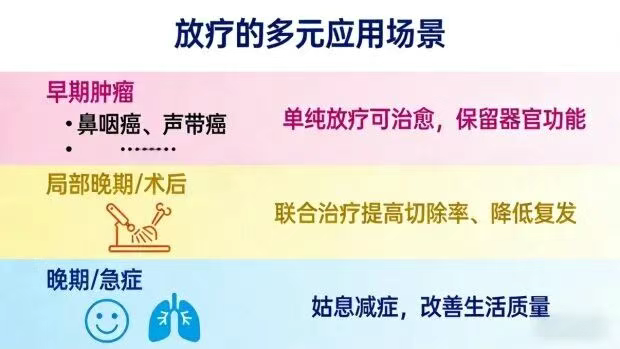
Early-Stage Tumors: Many early-stage tumors can be cured with radiotherapy alone while preserving organ function! For example, early-stage nasopharyngeal cancer, lymphoma, skin cancer, etc., allow patients to achieve long-term survival after radiotherapy. Early-stage vocal cord cancer, esophageal cancer, prostate cancer, and others show radiotherapy results comparable to surgery, while avoiding the regret of organ removal.
Locally Advanced Tumors: When combined with surgery and chemotherapy, radiotherapy can improve local tumor control. For instance, in advanced esophageal or rectal cancers that were initially difficult to surgically remove, radiotherapy can shrink the tumor—increasing the likelihood of successful surgical removal, reducing the risk of tumor spread during surgery, and significantly improving survival rates.
Advanced Tumors: As an important means of palliative symptom relief, radiotherapy can effectively alleviate patient suffering—such as relieving severe pain caused by bone metastases, managing cancerous bleeding, alleviating increased intracranial pressure due to brain metastases, and resolving breathing difficulties caused by tumor compression of the trachea. This helps improve the patient's quality of life and prolong survival.
Postoperative Adjuvant Therapy: After surgery for tumors such as lung cancer, breast cancer, or brain tumors, radiotherapy can eliminate potentially residual cancer cells, reduce the risk of recurrence, and improve survival rates. For example, in early-stage breast cancer, breast-conserving surgery combined with radiotherapy achieves the same effectiveness as radical mastectomy while preserving the breast, greatly boosting the patient's confidence.
Benign Diseases: Beyond tumors, radiotherapy can also treat some benign conditions! For example, postoperative radiotherapy can prevent scar hyperplasia, and radiotherapy for hemangiomas can occlude blood vessels and reduce the size of the lesions.
Important Reminder: Keep These Precautions in Mind After Radiotherapy!
Post-radiotherapy care directly impacts recovery. The precautions vary depending on the irradiated area and organ involved—be sure to pay close attention~
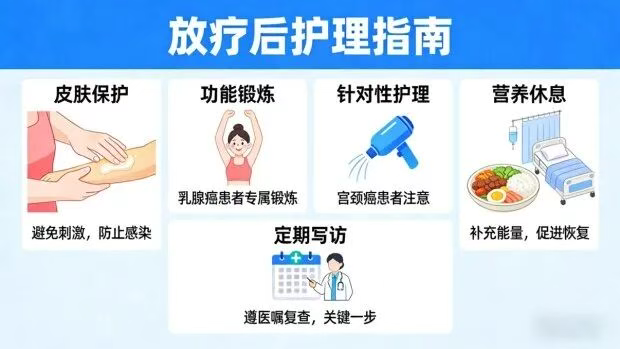
Protect the Treated Area: Normal tissues need time to heal after radiation, especially the skin. Avoid friction or irritation in the radiated area to prevent infection.
Consistent Functional Exercise: For example, after radiotherapy for breast cancer, patients should persistently perform lifting exercises for the affected arm to reduce swelling and prevent limited shoulder mobility.
Targeted Care: After radiotherapy for cervical cancer, regular vaginal irrigation is necessary to prevent adhesions and uterine infections.
Nutrition and Rest: Provide the body with adequate energy for recovery by maintaining proper nutrition and getting plenty of rest, while avoiding overexertion.
Regular Follow-ups: This is the most crucial point! Always adhere strictly to your doctor’s schedule for follow-up examinations to monitor recovery progress in a timely manner.
After reading this, do you now have a fresh understanding of radiotherapy? Radiotherapy is not a "scary beast," but an indispensable "precision tool" in cancer treatment.
If someone around you is facing choices in cancer treatment, consider sharing this article with them—to help more people move beyond misconceptions and view radiotherapy rationally. Wishing every patient the most suitable treatment plan and a swift recovery!
