Stop staying up late! The 5 "deadly" harms of chronic sleep deprivation
Stop staying up late! The 5 "deadly" harms of chronic sleep deprivation
"Just one more short video," "I'll sleep right after finishing this slide, no more delays" — does this sound like you every night, constantly pushing back bedtime with self-reassurance? Many believe staying up late isn’t a big deal, thinking an extra cup of coffee the next day will do the trick. However, what you may not realize is that chronic sleep deprivation is like a form of "slow self-destruction," quietly eating away at your health. Today, let’s dive into the overlooked dangers of staying up late and share practical ways to recover afterward. Be sure to save and share this with your night-owl friends!

Staying Up Late First "Attacks" Your Liver!
First and foremost, staying up late initially "targets" your liver! As the body's "detoxification expert," the liver silently processes metabolic waste every day, and its most critical repair period is between 11 p.m. and 3 a.m. If you're not asleep during this time, the liver's work rhythm is completely disrupted.
In the short term, you might notice severe bitterness or bad breath in the morning, a dull and sallow complexion, and even issues like constipation or diarrhea—all signs of declining liver function.
In the long run, the consequences could be far more serious: even if you don't drink alcohol, it could lead to fatty liver disease; worse yet, prolonged damage may gradually impair liver function, increasing the risk of hepatitis and liver cirrhosis. Don't force your liver to "work overtime" anymore!
Your Heart and Blood Vessels Can't Take It, and the Risk of Emergencies Soars!
Have you ever experienced this feeling: when staying up late into the early hours, do you suddenly feel your heart racing and your chest tightening? Actually, this happens because while staying up late, our bodies automatically enter a "stress state," causing blood pressure and heart rate to rise significantly compared to normal sleep.
If this state persists long-term, the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems are repeatedly "strained": high blood pressure and high cholesterol may follow, and you might even experience unexplained dizziness and chest tightness during the day. Even more dangerously, if you already have underlying conditions like hypertension or coronary heart disease, staying up late could directly trigger a myocardial infarction or stroke—the golden window for treating these emergencies is just a few minutes, and in severe cases, it can be life-threatening!

Your Immunity "Goes on Strike," Turning Minor Issues Into Major Problems
Sleep is like the "charging time" for our immune system. Only by getting a good night's rest can immune cells (such as white blood cells and lymphocytes) stay fully energized and help us fend off bacterial and viral invasions. However, when we stay up late, these "defensive soldiers" cannot properly "go on duty," and the body's "defensive wall" gradually weakens.
In the short term, you may notice that you catch colds or sore throats more easily, mouth ulcers keep recurring, and even allergic symptoms like itchy skin or sneezing worsen. Don’t assume these minor issues will simply pass with time—they are actually "warning signals" your body is sending you.
In the long run, staying up late persistently weakens the immune system. Not only does it increase the risk of autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, but it also makes it harder for the body to fight off cancer cells. Research shows that individuals who regularly stay up late have a 20%–30% higher risk of developing cancer compared to those with regular sleep patterns. This statistic is truly alarming and worth our vigilance!
Nervous and Endocrine Systems "Go Haywire," Leading to Emotional and Physical Breakdown
Staying up late doesn’t just harm your internal organs—it can also cause your nervous and endocrine systems to spiral “out of control,” throwing both your emotions and your body into chaos.
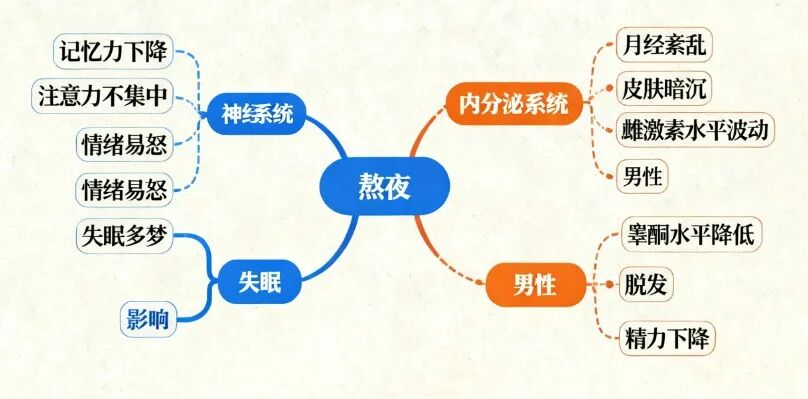
For the nervous system: Long-term sleep deprivation keeps the brain in a state of constant fatigue, paving the way for insomnia, anxiety, and depression. More noticeably, memory declines and reactions slow down. Many people feel their "brain is foggy" after a sleepless night, which is actually a sign that nerve cells are already "overdrawn."
For the endocrine system: Women may experience menstrual irregularities, delayed periods, reduced flow, and recurring breakouts. In severe cases, it could even trigger conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome, affecting fertility. Men, on the other hand, might see a drop in testosterone levels, leading to issues such as low energy and significant hair loss.
What's even more alarming is that these issues can form a vicious cycle: anxiety and insomnia make it harder to fall asleep, while physical discomfort fuels the urge to stay up late, gradually trapping you in the loop of "staying up late → experiencing problems → staying up even later."
Don’t Just "Fix" It Wrong After Staying Up Late! These 3 Methods Actually Work
Of course, everyone ends up staying up late occasionally. Rather than blaming yourself or feeling anxious, it's better to learn the right ways to recover. The core principle is: focus on improving **quality** over quantity, and reduce the burden on your body. Specifically, you can approach it from these three aspects:
Of course, everyone occasionally stays up late. Rather than blaming yourself or feeling anxious, it's better to learn the right recovery methods. The core principle is to prioritize **quality** over quantity of rest and reduce the strain on your body. Specifically, you can focus on these three aspects:
1. Sleep Recovery: Short naps are more effective than long, excessive sleep
After staying up late, avoid sleeping in for more than three hours during the day, as this can completely disrupt your nighttime sleep rhythm and make you feel even more exhausted. If you're genuinely tired during the day, take one or two short naps of 20–30 minutes each. After waking up, splash some cool water on your face to refresh yourself and avoid falling into deep sleep. In the evening, go to bed 1–2 hours earlier than usual. Close the curtains, wear earplugs, and create a dark, quiet environment to help your body enter deep sleep quickly.
2. Dietary Adjustments: Give your body a "quick recharge" of high-quality energy
- Stay hydrated: Staying up late can easily lead to dehydration. Drink a glass of warm water or lightly salted water upon waking up, and remember to hydrate frequently in small amounts throughout the day. Avoid sugary drinks.
- Eat nutrient-rich foods: For breakfast, opt for foods like eggs, milk, and whole-wheat bread to replenish protein and carbohydrates and quickly fuel your body. For lunch and dinner, eat more vegetables and fruits such as spinach, broccoli, and oranges to replenish vitamins and combat fatigue. Try to avoid greasy or spicy foods to prevent adding extra strain on your digestive system.
- Avoid "ineffective pick-me-ups": Try to steer clear of strong tea and coffee. If you really need an energy boost, limit yourself to one cup in the morning and avoid consuming any after 3 p.m. to prevent disrupting your sleep that night.
3. Light Activity: Simple movements to wake up your body's functions
Spend 5–10 minutes after waking up doing light activities like stretching, walking slowly, or simple yoga to boost blood circulation and alleviate stiffness and drowsiness. During work or study, stand up and move around for 2–3 minutes every hour—avoid sitting for too long. At night, soak your feet in warm water for 10 minutes before bed to help relax your body and mind and improve sleep quality.
In truth, the best way to recover is not to stay up late in the first place. Your body never lies—every late night will eventually "pay you back" in one way or another. Starting today, try putting down your phone and going to bed a little earlier. Your body will thank you for it!

