[Medical popular science] Radioactive Seed Implantation
Radioactive Seed Implantation
What is Radioactive Seed Implantation?
A precise form of radiotherapy that involves accurately implanting rice grain-sized I-125 radioactive seeds into tumors, allowing them to continuously release low-energy gamma rays within the body to directly destroy cancer cells. This is an internal form of precision radiotherapy (brachytherapy) and is internationally recognized as a minimally invasive cancer treatment.
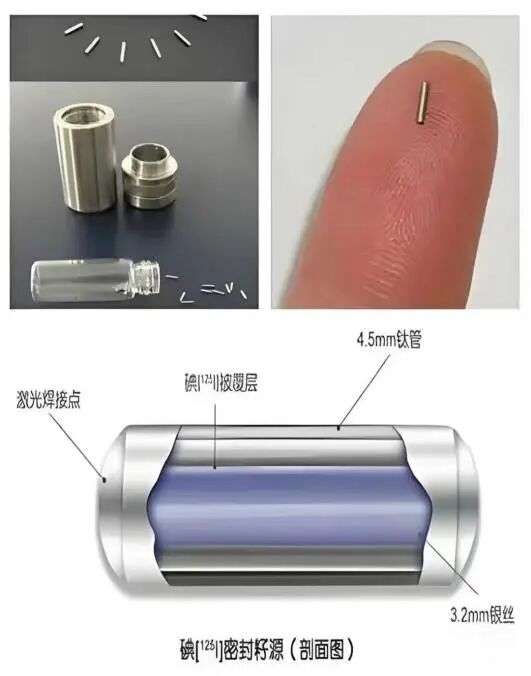

How does it kill tumors?
I-125 seeds release low-energy γ-rays (27–35 keV) with a range of only about 1.7 cm, capable of:
Providing stable radiation for 120–180 days
Equivalent to a precise radiotherapy robot "standing guard day and night" inside the tumor.
Directly damaging tumor cell DNA
Preventing replication and division, ultimately leading to cell death.
Concentrating the radiation dose within the tumor
The dose received by normal tissues is far lower than in the tumor area, ensuring high safety.
Avoiding major blood vessels and nerves
Without affecting the function of surrounding vital organs.
Therefore, it is often clinically described as: "an internal, close-range, and continuous miniature radiotherapy machine."

Why are more and more patients choosing Radioactive Seed Implantation?
Five Core Advantages
① Minimally invasive: Requires only 1–2 mm puncture points
Can be performed under local anesthesia with minimal trauma and quick postoperative recovery.
② Precise: Targets the inside of the tumor without harming normal tissue
Accurate seed placement under CT/ultrasound guidance, with an error margin of <1–2 mm.
③ Long-lasting: Continuously destroys tumors for up to six months
No need for daily hospital visits, unaffected by body position or breathing.
④ Safe: Limited radiation range and mild side effects
Rapid radiation attenuation with no impact on surrounding people.
⑤ Compatible with multiple treatment methods
Can be combined with surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, etc.
Highly suitable for patients who cannot undergo surgery, have recurrent tumors, or are in a weakened physical state.
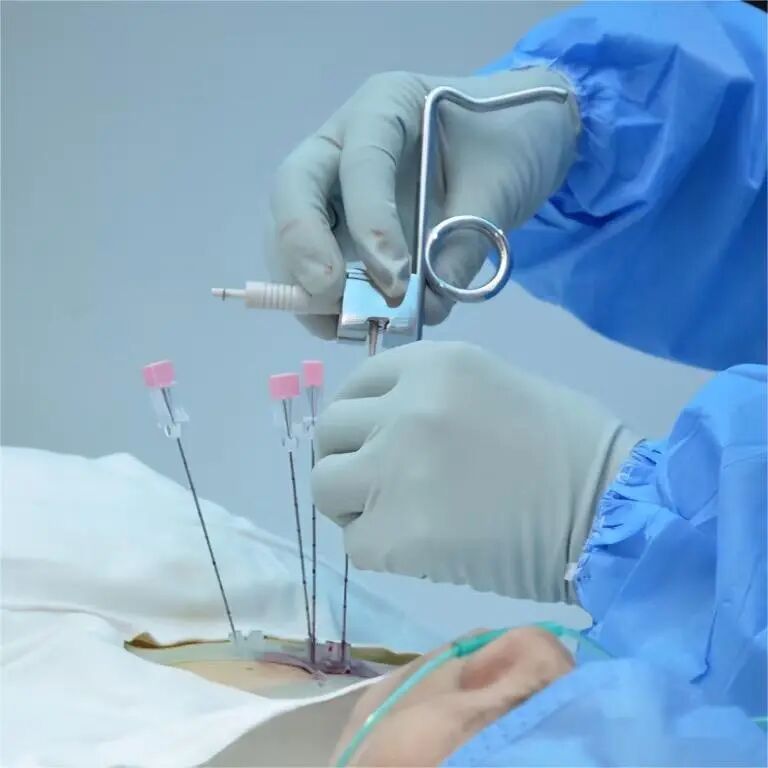
Which tumors are suitable for Radioactive Seed Implantation?
Most commonly used: Prostate cancer; lung cancer (solid nodules, obstructive tumors); pancreatic cancer; liver cancer (unresectable/postoperative recurrence); lymph node metastases (neck/mediastinum/abdomen); recurrent head and neck tumors; soft tissue sarcoma; postoperative recurrent lymph nodes in thyroid cancer; local recurrence of gastric or colorectal cancer.
Cancer pain control: For tumors compressing nerves or eroding bone tissue, radioactive seeds can effectively alleviate pain.
How is seed implantation performed? (Detailed procedure steps)
① MDT Multidisciplinary Evaluation
A team comprising oncology, interventional radiology, radiation oncology, and imaging departments jointly assesses:
- Tumor size and location relative to major blood vessels and nerves
- Suitability for percutaneous puncture
- Seed dosage and distribution plan (creation of a Treatment Planning System protocol)
② Development of Individualized Radiation Plan (TPS)
A medical physicist designs based on tumor morphology:
- Number of seeds
- Dosage per seed
- Distribution pattern
- Predicted dose distribution map
- This is the core of precision treatment.
③ Seed Implantation Procedure in the Operating Room (Minimally Invasive)
Under CT or ultrasound guidance, the physician uses an 18G or finer needle to:
- Precisely puncture the tumor
- Release seeds point by point according to the plan
- Perform real-time imaging verification to ensure compliance with the dose plan
- The entire procedure typically takes 30–60 minutes.
④ Post-procedure mobility is possible on the same day, with discharge typically achievable within 1–2 days. The treatment involves minimal trauma, promotes rapid recovery, and causes only mild pain.
⑤ The seeds continue to function within the body for over six months, eliminating the need for frequent hospital visits during the treatment period.
Minimally Invasive Interventional Department
The Minimally Invasive Interventional Department of Lanzhou Heavy Ion Center at Gansu Wuwei Cancer Hospital is led by President Wang Junjie and has been established with the recruitment of renowned minimally invasive interventional oncology specialists from within and outside the province. The department specializes in minimally invasive interventional therapies for tumors, complementing the limitations of traditional radiotherapy to form a comprehensive oncology treatment system.
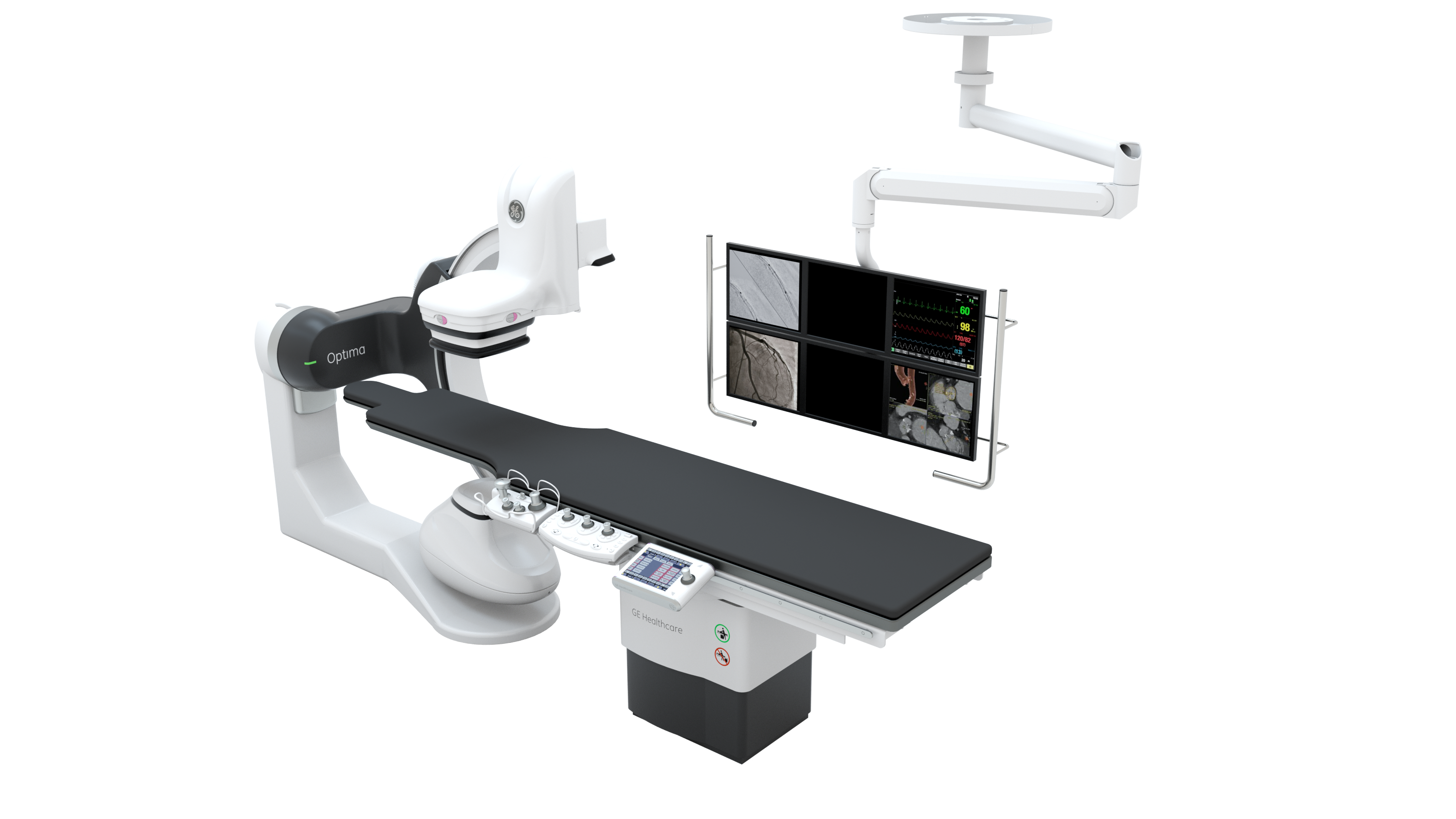

The department is equipped with 30 beds, offering a pleasant inpatient environment and comprehensive facilities. It is currently outfitted with advanced medical equipment, including a U.S.-made GE digital subtraction angiography (DSA) system, a large-aperture spiral CT scanner, microwave and radiofrequency coagulation devices, pulsed radiofrequency equipment, a radioactive seed implantation and planning system, high-definition ultrasound machines, and regional circulatory hyperthermic perfusion therapy systems. The department performs a wide range of minimally invasive procedures under DSA, CT, and ultrasound guidance for tumor treatment. Additionally, it conducts minimally invasive interventions for common vascular conditions such as major venous varicose veins, arteriovenous fistulas, diabetic foot, and other peripheral vascular diseases.
Inpatient Department of Lanzhou Heavy Ion Center, Gansu Wuwei Cancer Hospital
Representative Technologies of the Department
- Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for Tumors
- Hyperthermic Intrapleural Chemotherapy for Tumors
- Radioactive Seed Implantation
- CT-Guided Liver Tumor Ablation
- CT-Guided Microwave Coagulation Therapy for Pulmonary Nodules
- CT-Guided Cryoablation (Argon-Helium Knife) for Pulmonary Nodules
- Ultrasound-Guided Microwave Coagulation Therapy for Liver Nodules
- Ultrasound-Guided Thyroid Nodule Biopsy
- Ultrasound-Guided Axillary Lymph Node Biopsy
- Ultrasound-Guided Microwave Coagulation Therapy for Thyroid Nodules
- DSA-Guided Deep Vein Thrombectomy
- DSA-Guided Pulmonary Artery Embolization
- DSA-Guided Chemoembolization for Tumor Vasculature
- DSA-Guided Peripheral Vascular Angioplasty
- DSA-Guided Aneurysm Embolization
- Microwave Coagulation Therapy for Great Saphenous Vein
- DSA-Guided Arteriovenous Fistula Revision
- DSA-Guided Cerebral Angiography and Embolization
- DSA-Guided Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS)
