Heavy Ion Therapy Shows Over 80% Local Control in Pancreatic Cancer: US Center Data
Heavy Ion Therapy" vs. Pancreatic Cancer! US Cancer Research Center Releases Breakthrough Data,
Local Control Rate Exceeds 80%
Among all solid tumors, pancreatic cancer is often called one of the "toughest challenges" due to its insidious onset, rapid progression, and poor response to conventional treatments. Many patients are already inoperable at diagnosis, and traditional radiotherapy and chemotherapy have limited effectiveness, often leaving survival measured in months. However, in recent years, several leading cancer research centers in the United States have successively released the latest clinical data on heavy ion radiotherapy (Carbon Ion Radiotherapy), bringing unprecedented breakthroughs for this disease. The data show that in rigorously selected pancreatic cancer patients, heavy ion therapy achieves a local control rate exceeding 80%, with some patients achieving medium- to long-term survival and even experiencing significant tumor shrinkage or complete disappearance, offering new hope to pancreatic cancer patients worldwide.
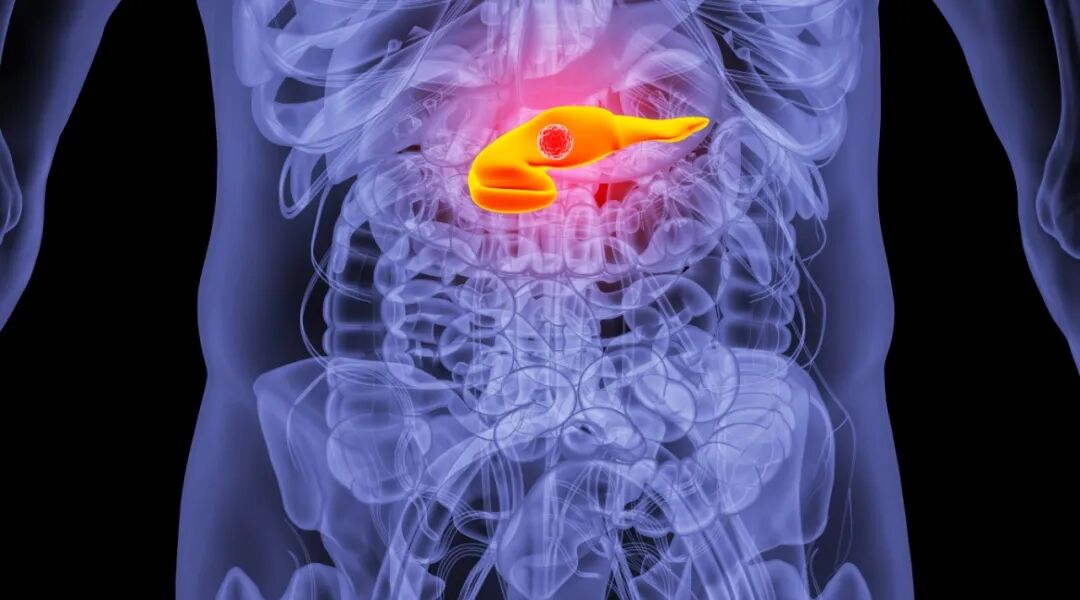
What exactly is heavy ion therapy?
How can it precisely "penetrate" pancreatic cancer?
Heavy ion therapy is an advanced radiation treatment technology. Unlike traditional X-rays or proton beams, heavy ion particles possess a higher biological effectiveness, releasing their maximum energy upon reaching the tumor depth—a phenomenon known as the "Bragg peak." This physical characteristic gives heavy ion therapy a natural advantage in treating pancreatic cancer, addressing its specific challenges such as deep-seated tumor location, surgical difficulty, and insensitivity to conventional radiotherapy.
Traditional radiotherapy continuously releases energy as it penetrates tissues, often unavoidably damaging healthy organs, especially around the pancreas where critical structures like the stomach, duodenum, liver hilum, and major blood vessels are concentrated. This imposes limitations such as "inability to irradiate aggressively." In contrast, heavy ion therapy can "lock" its energy within the tumor tissue, delivering powerful destruction to cancer cells while minimizing harm to surrounding healthy tissues. This precision allows doctors to safely increase the radiation dose within a certain range, thereby improving local control outcomes.
For highly radioresistant tumors like pancreatic cancer, the biological lethality of heavy ion therapy is nearly two to three times that of conventional X-rays, enabling it to combat cancer cells that are "insensitive" to traditional radiotherapy. This is also why studies from relevant U.S. centers have found that locally advanced pancreatic cancer patients treated with heavy ion therapy show significantly higher rates of tumor shrinkage and local control compared to those receiving conventional treatments.
Latest US data shows:
Local control rate exceeds 80%, treatment window redefined
According to follow-up data from a U.S. heavy ion research team on patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer, heavy ion radiotherapy not only effectively reduces tumor size but also extends local control duration. Published authoritative data shows that over 80% of patients achieved local lesion stabilization or even shrinkage one year later, with some cases demonstrating significant tumor necrosis. This has also enabled certain patients initially deemed inoperable to meet the criteria for surgical resection in subsequent evaluations.
This implies that pancreatic cancers previously considered "inoperable" may now regain surgical eligibility due to tumor volume reduction, decreased infiltration, and reduced vascular encasement. For pancreatic cancer, the availability of surgical opportunities is often associated with improved overall survival. Therefore, the emergence of heavy ion therapy essentially reshapes the "window of curability" for some patients.
Notably, due to its precise dose coverage and concentrated energy delivery, the incidence of severe adverse reactions in heavy ion therapy is significantly lower than that of traditional radiotherapy. Many patients can resume eating and light activities shortly after treatment, with overall quality of life largely unaffected. Clinical feedback indicates that the vast majority of patients tolerate the treatment well, which is a key reason for its rapid international recognition and adoption into clinical practice.
Why is heavy ion therapy experience noteworthy?
While Japan and Germany started heavy ion therapy earlier, China's advantage lies in its rigorous patient selection mechanisms, advanced imaging fusion planning, and concurrent research integrating immunotherapy and precision chemotherapy, contributing to a more mature overall efficacy system. At the Gansu Wuwei Cancer Hospital's Wuwei Heavy Ion Center and Lanzhou Heavy Ion Center, heavy ion treatment plans are typically developed collaboratively by multidisciplinary teams to ensure each patient receives the most reasonable dose design and treatment course planning.
Particularly in the field of pancreatic cancer, long-term follow-up studies on changes after heavy ion therapy—including reduced tumor metabolic activity, increased tumor cell apoptosis, and altered local blood flow—have provided critical evidence for subsequent treatment. It is this accumulation of rigorous data that has gradually positioned China's heavy ion technology as one of the internationally influential treatment modalities.
For patients seeking the latest treatment options within top-tier global medical systems, undergoing a heavy ion therapy evaluation can help identify a more personalized treatment pathway. Especially for pancreatic cancer cases where the tumor is progressing rapidly locally, traditional treatments are ineffective, or side effects are intolerable, heavy ion therapy offers a safer and more effective localized treatment approach.

Which pancreatic cancer patients should consider heavy ion therapy?
Not all pancreatic cancer patients are suitable for heavy ion therapy, but the following groups should especially consider learning about it promptly and seeking consultation:
- Locally advanced, inoperable cases (with tumor encasing blood vessels) involving vascular invasion;
- Patients who respond poorly to conventional treatments, with rapidly progressing tumors;
- Those in weak physical condition who cannot tolerate major surgery;
- Patients hoping to reduce tumor size to potentially become eligible for surgery;
- Individuals who have undergone multiple lines of chemotherapy with limited effectiveness.
However, any personalized treatment plan must be evaluated by a professional team. It should not be assumed that heavy ion therapy can "100% replace surgery" or is "completely free of side effects." Heavy ion therapy is a precise yet powerful tool that must be used with caution—only through strict patient selection can its maximum value be realized.

Heavy ion therapy is rewriting the future of pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer is not without options, nor does it solely rely on enduring traditional treatments. The latest data on heavy ion therapy released by the United States has revealed another possibility: precise, effective, well-tolerated, and with significantly improved local control rates. For many patients who previously had no surgical options or for whom conventional treatments were ineffective, heavy ion therapy is like a beam of light piercing through the darkness, offering them the chance for a longer and higher-quality life.
If you know someone battling pancreatic cancer who is facing treatment decisions, it is crucial to actively explore the latest international treatment options. Whether heavy ion therapy is suitable for an individual must be determined through a comprehensive evaluation by a professional medical team. However, taking timely action at the right moment often means greater hope.
