A Case Comparison of Heavy Ion and X-ray Radiotherapy Plans for a Brain Glioma Patient
A Case Comparison of Heavy Ion and X-ray Radiotherapy Plans for a Brain Glioma Patient
Glioma refers to a tumor originating from glial cells in the brain and is the most common primary intracranial tumor. The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of central nervous system tumors categorizes gliomas into grades I to IV, with grades I and II being low-grade gliomas, and grades III and IV being high-grade gliomas
It is well-known that complete surgical removal of all brain tumors is difficult, and postoperative recurrence is highly likely. Radiotherapy is essential after surgery for grade II, III, and IV gliomas, particularly for high-grade gliomas (grades III and IV) .Traditional X-ray radiotherapy for postoperative glioma has suboptimal efficacy and causes significant damage to normal tissues. In contrast, heavy ion radiotherapy, due to its radiophysical and biological characteristics, allows for better concentration of the dose on the tumor site. The dose at the front and end of the tumor is much lower than that of X-rays, enabling heavy ion radiotherapy to fundamentally eradicate the tumor and better protect the surrounding intricate normal tissues.
Since the opening of the Heavy Ion Center at Gansu Wuwei Cancer Hospital in April 2020, it has admitted 8 postoperative glioma patients, all with excellent therapeutic outcomes. This paper presents a dosimetric comparison for one glioma patient treated at our center, comparing plans designed for heavy ion two-dimensional conformal (2D) therapy and linear accelerator X-ray intensity-modulated conformal (IMRT) therapy
Patient: Female, 25 years old, status after surgery for left frontal lobe diffuse astrocytoma, WHO grade II, KPS score 80. Planning target volume (PTV), prescription dose 54 Gy (heavy ion Gy(RBE)/18 fractions), requiring 100% dose coverage of 95% of the target volume
Heavy Ion Planning System: ciPlan V1.0
X-ray Planning System: Eclipse 15.6
1.Dose Distribution Cloud Map
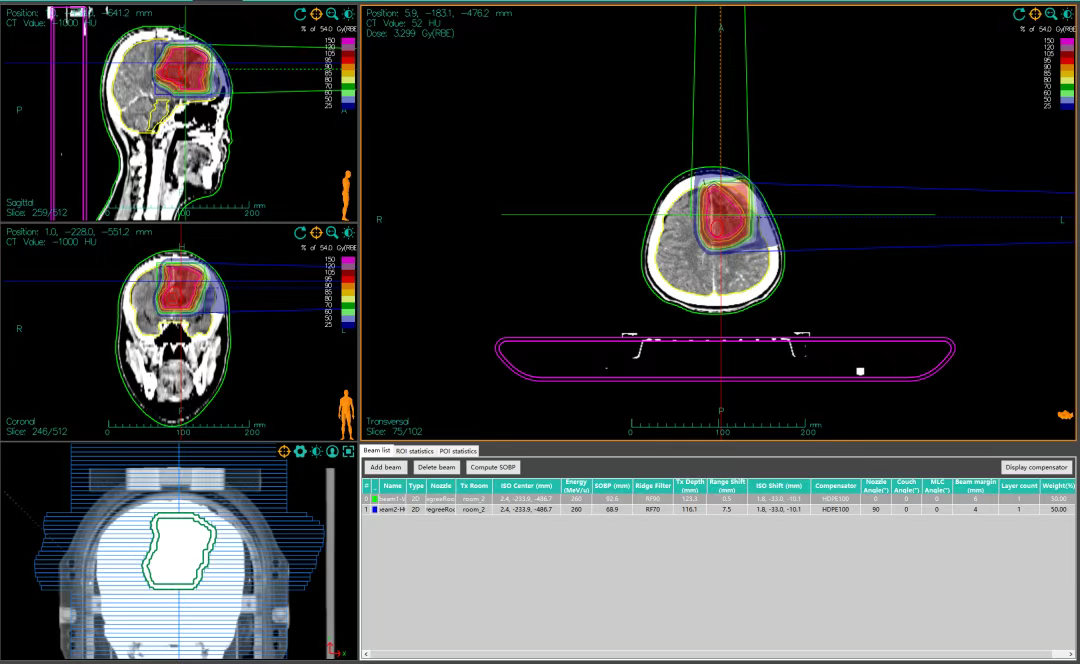
Figure 1 Dose cloud distribution of the heavy ion 2D plan for this patient (displaying an initial dose of 25% of the prescription dose).
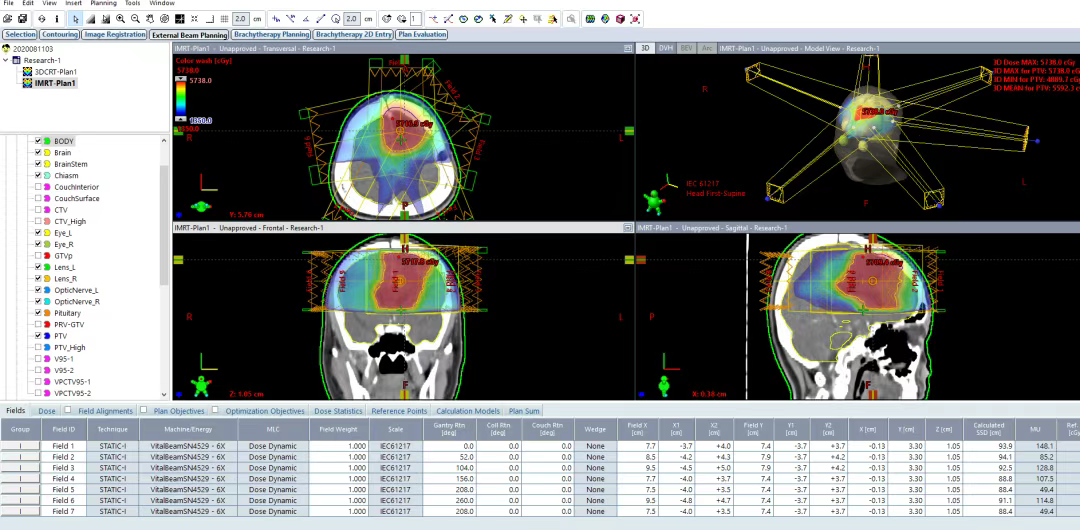
Figure 2 Dose cloud distribution of the IMRT plan for this patient (displaying an initial dose of 25% of the prescription dose).
It can be clearly seen from the figures that when the target dose meets the prescription dose, the heavy ion 2D plan uses fewer radiation fields than the IMRT plan. The low-dose radiation area is smaller, and the irradiation range to normal brain tissue is significantly smaller than that of the IMRT plan. This indicates that compared to traditional X-ray radiotherapy, heavy ion radiotherapy has significant advantages in radiophysics and biology, allowing for better dose concentration on the tumor site and better protection of the surrounding normal tissues.
2.Comparison of Dose Distribution to Organs at Risk and Number of Radiation Fields (unit: cGy)From the table, it can be concluded:
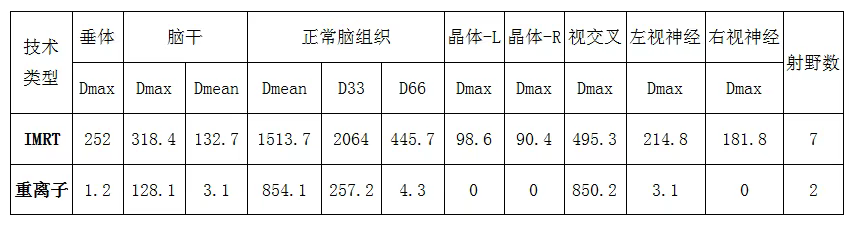
1.When the target dose meets the prescription dose, the heavy ion conformal plan uses fewer radiation fields than the IMRT plan. Fewer radiation fields result in a smaller surrounding radiation area, which is more conducive to protecting the surrounding normal brain tissue.
2.Regarding normal tissues, the dose received by most normal tissues and organs at risk in the heavy ion conformal plan is far less than that in the traditional X-ray IMRT plan. The dose to normal tissues in the IMRT plan is several times even hundreds of times higher than that in the heavy ion conformal plan. Some surrounding organs at risk may even receive no irradiation when using the heavy ion conformal plan, such as the lens and right optic nerve in this case.
Studies indicate that heavy ion radiotherapy for glioma has no significant side effects, does not affect patients' intellectual function, and spatial cognition, attention, memory, and executive function remain within a good range, with a favorable prognosis
In summary, radiotherapy is an important means of tumor treatment. Compared with conventional radiotherapy, the advantages of heavy ion therapy for brain tumors are as follows:
1.Immediate noticeable effects, significant reduction of edema.
2.Good dose inversion of carbon ions, accurately killing tumors.
3.Carbon ions minimize brain damage and can deliver a higher dose to the tumor.
4.Toxicity and side effects related to carbon ion radiotherapy are relatively small.
5.Carbon ions have a stronger radiobiological effect in killing tumors, and are more effective against tumors resistant to photon radiotherapy.
Consultation and Appointment
Director Wu: +86 13909357563
Dr. Yan: +86 13893552066
Telephone: 0931-2122056
Address: Lanzhou Heavy Ion Consultation Office, No. 738, Nanchang Road, Chengguan District, Lanzhou, Gansu Province
Preliminary Review: Zhang Lihong
Final Review: Zhang Jie
