"Guardian of the Neck" – Vigilant Protection, Strengthening the Defense Line for Throat Health.
"Guardian of the Neck" – Vigilant Protection, Strengthening the Defense Line for Throat Health.
Head and neck cancer ranks as the sixth most common malignancy globally, with over 900,000 new cases diagnosed each year. Alarmingly, nearly half of the patients are already at an advanced stage when they first seek medical attention, often missing the optimal window for treatment. Today, we will delve into head and neck cancer—understanding what it is, and how to detect, examine, treat, and prevent it.
I. What are Head and Neck Tumors?
As the name suggests, head and neck tumors develop in regions of the head and neck. Specifically, these tumors commonly occur in the following sites: the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses; the oral cavity, including the tongue, gums, and floor of the mouth; the throat area, including the tonsils, pharynx, and larynx; the salivary glands, such as the parotid and submandibular glands; as well as the thyroid gland and lymph nodes in the neck.
Among head and neck tumors, thyroid cancer, laryngeal cancer, nasopharyngeal cancer, hypopharyngeal cancer, and tonsillar cancer are relatively common.
The anatomical structures where these tumors are located are complex and involve vital functions related to breathing, swallowing, vocalization, and facial appearance. Precisely because of their special location, patients not only face threats to their life safety but also endure the dual impact of the disease itself and the alterations to normal bodily functions caused by changes in anatomical structure during treatment.
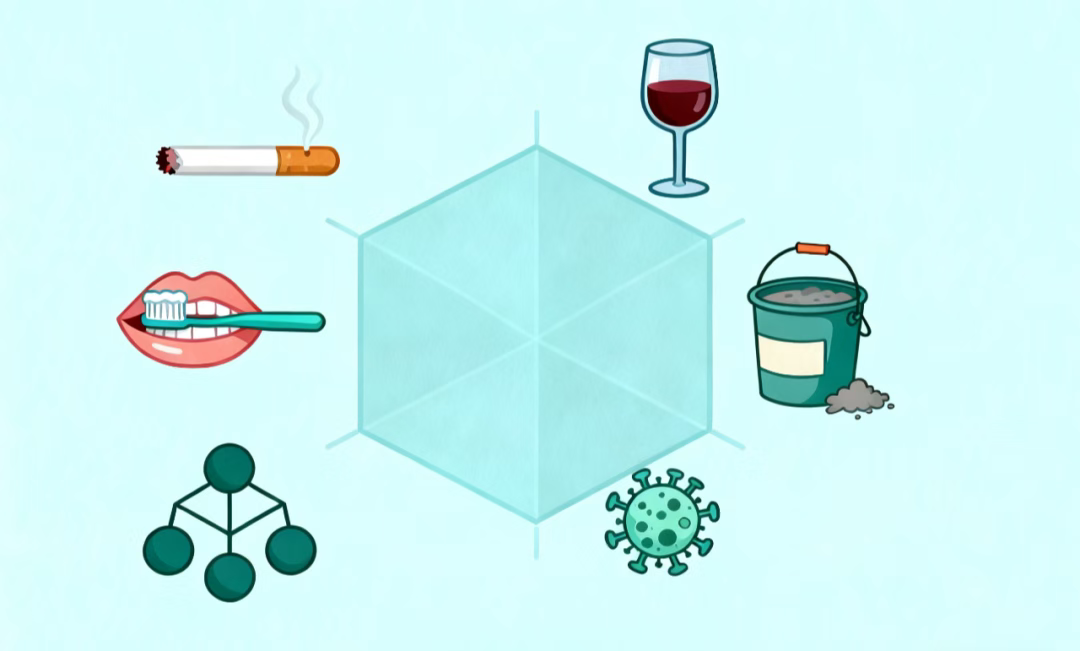
II. Who Should Be Particularly Vigilant About These Types of Tumors?
1.Long-term smokers: Carcinogens in cigarettes directly affect the throat and oral cavity, posing health risks.
2.People who frequently consume large amounts of alcohol: Alcohol significantly increases the risk of cancer.
3.Individuals with poor oral hygiene or those with oral ulcers of unknown cause are also in the high-risk category.
4.People frequently exposed to chemicals such as paint, wood dust, or industrial dust should also be cautious.
5.Individuals with a family history of cancer.
6.Those infected with viruses like EB virus or HPV are also considered "high-risk groups" for head and neck tumors.
People in these categories are advised to undergo regular health check-ups and proactive screening.
III. What are the potential early signs of head and neck tumors?
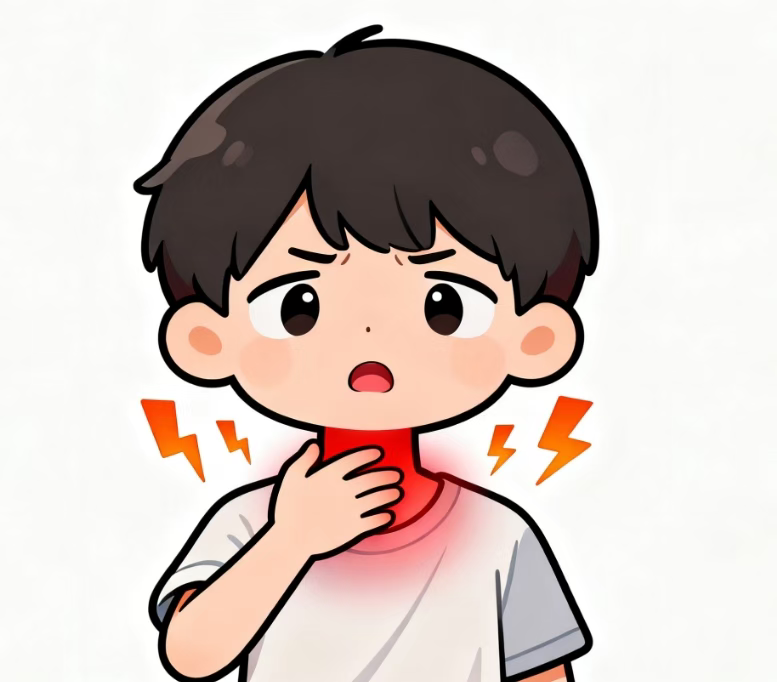
Early symptoms of head and neck tumors are often subtle and easy to miss, but the body may send early "alerts" through certain abnormalities
1.Hoarseness lasting more than two weeks? This requires particular attention, as it could be a signal of laryngeal cancer.
2.Frequent throat pain or a persistent feeling of something stuck in the throat? Don't always dismiss it as mere "internal heat"; there might be more serious health issues needing attention.
3.Ulcers, white patches (leukoplakia), or red patches (erythroplakia) inside the mouth that don't heal for a long time? One must be highly vigilant about such conditions and not take them lightly.
4.Frequent nasal congestion, occasional nosebleeds, or sensations of ear fullness and hearing loss? These discomforts may be related to the health of the nasopharynx.
5.Feeling a hard lump in the neck that isn't painful but doesn't go away? This situation should not be delayed; seek to identify the cause promptly.
6.Difficulty swallowing food, slurred speech, or frequent tinnitus? Once these symptoms appear, it is necessary to seek medical examination promptly.

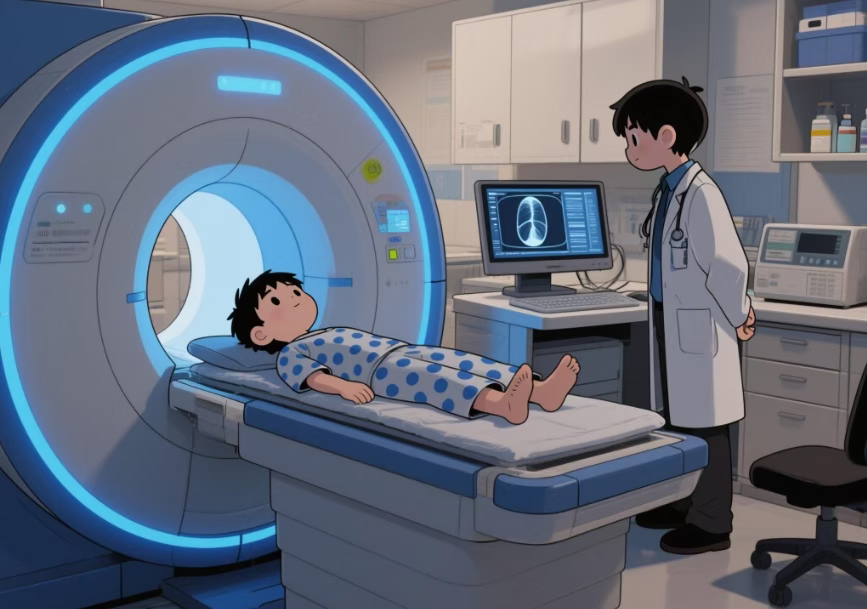
IV. How are head and neck tumors examined?
When relevant symptoms appear, doctors will arrange examinations based on specific manifestations. Common methods include: first using an endoscope to look deep inside the throat or nasal cavity for a direct view; then using imaging techniques like CT, MRI, or ultrasound to determine the tumor's approximate location and actual size; the key step for confirmation is a pathological biopsy—taking a small tissue sample from the suspected area for analysis to determine if the tumor is malignant. If there are nodules on the thyroid gland or a palpable mass in the neck, color Doppler ultrasound is typically prioritized for initial investigation, and a puncture biopsy may be performed if necessary to further clarify the nature.
V. What treatment options are available?
Treatment plans for head and neck tumors are developed by doctors considering factors like the tumor's location and disease stage. Common treatment modalities mainly include the following categories.
1.Surgical resection: Conditions like laryngeal tumors or thyroid nodules are often treated by directly removing the lesion surgically. Sometimes, concurrent neck lymph node dissection is necessary to reduce the risk of spread.
2.Radiation therapy: This treatment method is particularly effective for certain types of head and neck tumors like nasopharyngeal cancer and laryngeal cancer. It can precisely target and "irradiate" the tumor tissue, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy cells as much as possible.
3.Chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy: These treatments are often used for patients with advanced disease or recurrence after initial treatment. They are frequently combined with surgery or radiotherapy based on the specific clinical situation to enhance treatment efficacy.
It is particularly important to note that the earlier head and neck tumors are treated, the less treatment burden the patient bears. Many early-stage head and neck tumors can be effectively controlled with minimally invasive surgery or radiotherapy alone, and patients have a relatively higher five-year survival rate.
VI. How to prevent head and neck tumors?
1.Take the initiative to quit smoking and control alcohol intake to reduce exposure to potential cancer-causing factors from the source.
2.Maintain daily oral hygiene, insist on cleaning the mouth every day, and regularly go to the hospital for dental cleanings and oral check-ups.
3.If exposure to toxic gases or dust is necessary in work or daily life, take protective measures to reduce health risks associated with the occupational environment.
4.Get vaccinated against HPV based on individual circumstances; this vaccine can help prevent some types of oropharyngeal cancer.
5.If abnormal symptoms in the head and neck area are noticed, seek medical examination promptly without delaying treatment.
People who belong to high-risk groups for head and neck tumors are advised to undergo specialized head and neck health screening once a year.
Early detection, early treatment – head and neck tumors can be overcome!
Hoping everyone gains more awareness and early protection,
paying attention to their own and their family's head and neck health.
Preliminary Review: Zhang Lihong
Final Review: Zhang Jie
