A patient, male, 54 years old, was diagnosed as pancreatic cancer with liver metastasis
Patient, male, 54 years old, diagnosis: pancreatic cancer with liver metastasis.
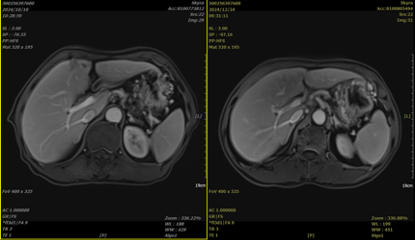
Medical history: The patient developed upper abdominal pain without apparent provocation in April 2024. At that time, it was not taken seriously, and no treatment was administered. Subsequently, the patient noticed a gradual worsening of the pain, which became continuous and was accompanied by back pain. On September 28, 2024, the patient sought medical attention at a local hospital. An abdominal MRI revealed an irregular mass with mixed signals of slightly long T1, slightly long T2, and long T1, long T2 in the tail of the pancreas. The DWI showed high signals, with unclear boundaries and blurred surrounding fat layers. The mass was closely related to the adjacent gastric wall, measuring approximately 5.6cm x 3.4cm x 2.8cm. It involved the splenic vein and artery, leading to pancreatic portal hypertension; a small amount of ascites was present; multiple abnormal enhancing lesions were observed in the liver; and multiple small lymph nodes were found around the pancreas and in the retroperitoneum, with some indicating possible metastasis. A PET-CT scan showed an irregular soft tissue density mass in the tail of the pancreas with abnormally increased FDG uptake, SUVmax 6.1, measuring approximately 5.6cm x 3.7cm x 3.8cm. The lesion had unclear boundaries, with indistinct separation from the adjacent gastric wall in the front and the splenic vein and artery in the back. Multiple lymph nodes with increased FDG uptake, SUVmax 2.0, the largest with a short diameter of approximately 0.7cm, were seen around the pancreatic lesion, in the hepatogastric space, and in the retroperitoneum. Multiple nodular areas of increased FDG uptake were observed in the liver parenchyma, with some slightly hypodense nodules visible on the same CT scan, particularly in the left outer upper segment, SUVmax 3.5, the largest measuring approximately 1.2cm in diameter. On October 8, 2024, the patient was admitted to our hospital. After admission, relevant examinations were completed. A puncture biopsy of the lesion in the tail of the pancreas indicated moderately differentiated pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Immunohistochemical results showed: C-erbB-2 (0), CK19 (+), CK20 (-), CK7 (+), Ki-67 (positive rate ≈ 30%), P53 (missense mutation), S100p (weak +). MLH1 (+), MSH2 (+), MSH6 (+), PMS2 (+). Gene testing revealed a KRAS G12V mutation. After a definitive diagnosis, the patient received carbon ion radiotherapy for pancreatic cancer and liver metastasis, with a total dose of PTV1 40Gy(RBE)/10Fx, PTV2 8Gy(RBE)/2Fx, PTV3 8Gy(RBE)/2Fx, PTV4 44Gy(RBE)/11Fx, and PTV5 16Gy(RBE)/4Fx. Concurrently, starting from October 12, 2024, the patient received systemic intravenous chemotherapy with "albumin-bound paclitaxel + gemcitabine". A follow-up abdominal MRI on November 12, 2024, showed post-treatment changes in pancreatic cancer. The cystic-solid mass in the tail of the pancreas had unclear boundaries with the adjacent gastric wall and splenic vein and artery. Compared to the previous scan (October 10, 2024), the lesion had decreased in size. Multiple abnormal enhancing nodules were observed in the liver, most likely representing metastases, which had partially decreased in size. Multiple lymph nodes were found in the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneum, which had also partially decreased in size.
Treatment plan: Carbon ion radiotherapy for pancreatic cancer with a total dose of 56Gy (RBE)/14Fx; Carbon ion radiotherapy for liver metastasis with a total dose of 60Gy (RBE)/15Fx; Concurrent chemotherapy with albumin-bound paclitaxel + gemcitabine.
Treatment effect: